Form Submission
Note: Spartacus 4.x is no longer maintained. Please upgrade to the latest version.
Note: Spartacus 4.x was tested with SAP Commerce Cloud versions 1905 to 2205. Spartacus 4.x has not been verified to work with (and is not guaranteed to work with) SAP Commerce Cloud 2211 or later releases.
This page explains how to persist form-data content in a database when the submission of a form is triggered from the “outside”.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Submitting a form from the “outside” means that you can submit a form from one component, although the submit button (i.e., the trigger for saving the form) is in a completely different, independent component. This approach allows you to implement different types of logic models after you submit the form. That logic can be as simple as a redirection to a web page, or something more complex such as calculation.
In Angular, the most common way for a component to share data and information with another component is by passing data or events. There are two different approaches to this:
- A component can be used inside another component, thus creating a hierarchy (e.g., child components using @Input and @Output decorators).
- Communication can be established using observable and subjects. This is the most common way for communication between components when they are not aware of each other or do not share a direct parent/child relationship.
In the FSA SPA application, the second approach has been used to implement form submission logic and this page explains that approach.
Executing Form Data Submission
The idea is to create a BehaviorSubject to pass values inside. Every time the stream changes, the observer will know about it and execute the callback function (update/save of formData).
We created a submittedForm BehaviorSubject in form data service and a method submit() which is used to add formData to the BehaviorSubject stream.
export class FormDataService {
submittedForm = new BehaviorSubject<YFormData>(null);
submit(form: YFormData) {
this.submittedForm.next(form);
}
...
}
The same service also exposes the public method getSubmittedForm(), with whom we can subscribe to newly submitted forms in any component using the method.
The following example shows the FNOLNavigationComponent where we subscribed to the submitted form and used its data to update the claim during navigation to the next FNOL step.
@Injectable()
export class FormDataService {
submittedForm = new BehaviorSubject<YFormData>(null);
submit(form: YFormData) {
this.submittedForm.next(form);
}
getSubmittedForm(): Observable<YFormData> {
return this.submittedForm.asObservable();
}
...
}
@Component({
selector: 'cx-fs-fnol-navigation',
templateUrl: './fnol-navigation.component.html',
})
export class FNOLNavigationComponent implements OnInit, OnDestroy {
next(currentStep: number, claimData: any): void {
...
this.subscription.add(
// Subscribe to the data to get newly emitted value
this.formDataService
.getSubmittedForm()
.pipe(
switchMap(submittedFormData => {
if (submittedFormData && submittedFormData.content) {
claimData.configurationSteps[
this.activeStepIndex
].stepContent.contentData = submittedFormData;
this.claimService.updateClaim(
claimData,
this.activeStepIndex,
StepStatus.COMPLETED
);
}
return of(null);
})
)
.subscribe()
);
}
}
In short, this means that components will trigger form data persistence using the submit method (which will emit new form data with the mandatory formDataId attribute). In dynamicforms library components, we will subscribe to this change, check if the form’s content is valid, and eventually save the form.
NOTE: This also means that the dynamicforms library is responsible for saving form data in a database. However, the starting point for saving form data is a custom component (fsastorefrontlib) which emits a new value to the submittedForm stream.
@Component({
selector: 'cx-fs-fnol-navigation',
templateUrl: './fnol-navigation.component.html',
})
export class FNOLNavigationComponent implements OnInit, OnDestroy {
constructor(
...
protected formDataService: FormDataService,
) {}
next(currentStep: number, claimData: any): void {
const formData: YFormData = {};
if (this.activeStepData.yformConfigurator) {
formData.id = this.activeStepData.yformConfigurator.id;
}
// Emit new value to submittedForm stream
this.formDataService.submit(formData);
// Subscribe to changes handled in dynamicformslib and execute additional logic
this.subscription.add(
this.formDataService
.getSubmittedForm()
.pipe(
switchMap(submittedFormData => {
updateClaim...
})
)
.subscribe()
);
}
}
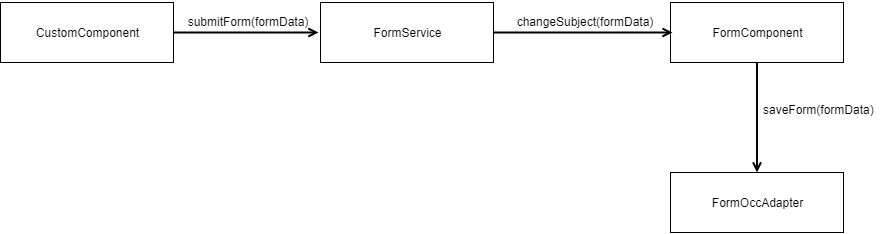
Submission Flow Example
The following diagram illustrates an example of a form submission flow: