How to retrieve JSON Web Tokens (JWT)
Overview
A JSON Web Token (JWT) is a standardized object containing some structured information. A JWT contains three parts:
- Header: Containing meta information like hashing algorithm and verification certificates
- Payload: The actual data
- Signature: Signature of the Header and Payload for verification
Given a JWT, you can use the information from the header and signature to check if the JWT is valid. Therefore, JWTs are used to exchange authorization and authentication information between applications.
JWT on SAP BTP
The retrieval of a JWT is done by the approuter together with the XSUAA. We explain these concepts in this guide . Find a complete setup in the sample applications for Cloud Foundry and k8s. The flow is as follows:
- user requests a resource and is not yet authenticated
- approuter redirects the request to the identity provider (IdP)
- XSUAA issues a JWT - see here for details
- approuter adds the JWT to the request headers and redirects the request to the initially requested resource
A JWT issued this way contains a JKU header property.
This property points to the URL where you can obtain the certificate to verify the JWT.
The URL must be from the XSUAA domain so that it is trusted and the JWT validation does not fail.
Sometimes you want to use a JWT which is not issued by the XSUAA and approuter.
Such tokens do not contain a JKU at all or a value with a different domain.
In this case the SAP Cloud SDK does not validate the token, but the destination service does.
You have to set the destination properties x_user_token.jwks or x_user_token.jwks_uri to provide the information to verify the custom JWT.
If you use a custom JWT without the approuter and XSUAA service, it is your responsibility to do the access control in the application.
A JWT has a limited lifetime but is nevertheless a sensitive security object. Do not log complete JWTs in the application, share them with others, or use online tools to decode them.
Use JWT in Application
After the JWT was issued, it is added to the request headers by the approuter:
{
"headers": {
"authorization": "Bearer yourJwtTokenBase64Encoded"
}
}
The SAP Cloud SDK has a convenience function to extract the JWT from the request object. For NestJS, the code would look like:
import { Controller, Get, Req } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Request } from 'express';
import { retrieveJwt } from '@sap-cloud-sdk/core';
@Controller()
export class AppController {
constructor() {}
@Get('some-sample-endpoint')
getSomeSampleEndpoint(@Req() request: Request): Promise<void> {
const myJwt = retrieveJwt(request);
//Do something with the JWT e.g. fetch some data using a destination
}
}
Note, that the SAP Cloud SDK uses the IncomingMessage object from node, which is compatible to the request object of common frameworks like express or NestJs.
In case you use a different framework, the implementation in the retrieveJwt() is simple.
Effectively it takes authorization header value and extracts the token value.
You can use the JWT to call the destination service or make a request against a destination directly.
Note, that the destination service performs token exchange flows for you, if configured accordingly.
This means the initial JWT is transformed to a SAMLBearerAssertion or ClientCredentials grant.
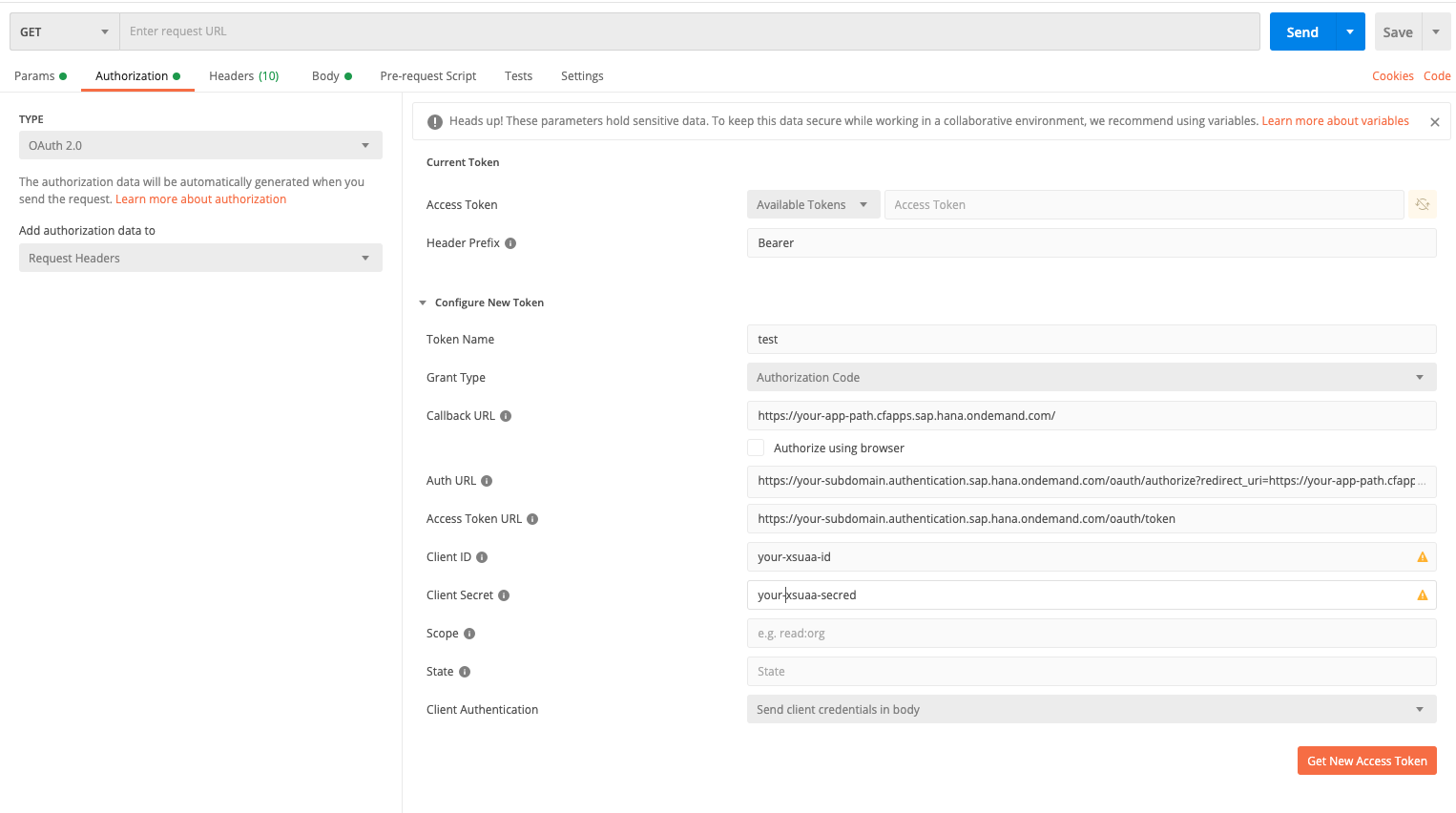
Obtain JWT with Postman
For a faster feedback cycle, it is convenient to test things locally without deployment to the SAP BTP. In some cases, applications rely on a JWT to set scopes or propagate a user to external systems. In such a case, you can obtain the JWT using Postman:
- create a new request
- go to the "Authorization tab of the request
- select "OAuth 2.0" as a type
- fill the following values in the user interface:
Callback URL: Path to the application protected by the XSUAAAuth URL: Path to the authentication endpoint using your subdomain and the values for the callback URL e.g.https://<subdomain>.authentication.sap.hana.ondemand.com/oauth/authorize?redirect_uri=<callbackUrl>Token URL: Path to the token endpoint using your subdomain, e.g.,https://<subdomain>.authentication.sap.hana.ondemand.com/oauth/tokenClient IDandClient secretfor the XSUAA service (either VCAP variables or service keys)- uncheck the
Authorize using browser checkbox
- press the
Get new access tokenbutton to retrieve a token - Postman will open a window showing the IdP login form
- enter username and password
- Postman shows the retrieved token that you can copy
Cookies will remember the entered username and password. This makes re-fetching a new token super quick when your old token expires. Remove the cookies in case you want to start fresh.
Obtain JWT programmatically
In some situations, it is necessary to retrieve a JWT programmatically. We have implemented the OAuth 2.0 flow for our internal E2E tests and the implementation involves many steps. We will give a high-level overview.
- retrieve a
codefrom the XSUAA - initial GET request on XSUAA:
https://<xsuaaUrl>/oauth/authorize?client_id=<clientId>&redirect_uri=<redirectUri>&response_type=code - This will provide cookies for all upcoming XSUAA requests.
- retrieve a SAML request from the XSUAA:
https://<xsuaaUrl>/saml/login/alias/<subdomain>.<host> - Transform the SAML request into a SAML response via the IdP.
This involves multiple redirected requests with a lot of cookies and request parameters passed around.
In the browser redirects with the
set-cookieandlocationheaders work well. In node, most HTTP clients do not handle the redirects correctly and a manual redirect on 302 response needs to be implemented. - Once you have the SAML response, call the XSUAA to retrieve the
codein the location header. - Use the
codewith clientId and clientSecret to get a JWT token from the XSUAA service.
In case you also need an implementation, investigate the steps in the debug console of your browser when you login.