Load Service Bindings within various Environments
Load Service Binding Information
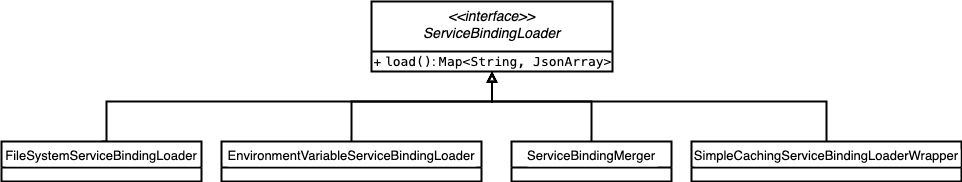
SAP Cloud SDK provides functionality to load service binding information when running the application in any Cloud Foundry and Kubernetes (in particular Gardener) environment. Below you can find an architectural overview of the relevant classes.
Please note that the API is currently in an experimental state.
Let's look at the classes and their use cases individually.
ServiceBindingLoader
This interface offers only one method to load the existing service bindings for the current application.
The abstract method named load() will have different functionality based on the subclass.
The following four classes implement this interface.
FileSystemServiceBindingLoader
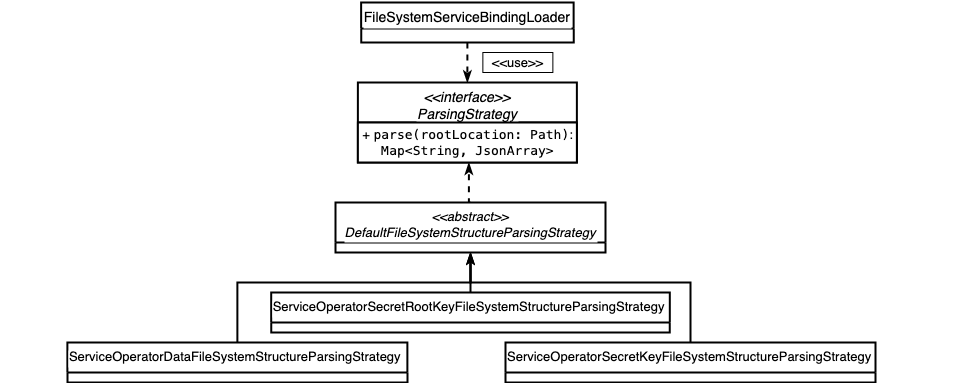
This class is used for transforming file system structures (e.g. files and directories) into service bindings, starting at a specific root location based on the provided ParsingStrategy.
It has a Functional Interface (ParsingStrategy), exposing the Map<String, JsonArray> parse(Path) method.
FileSystemServiceBindingLoader.ParsingStrategy represents an algorithm to transform a given root location (the directory in the file system) to service bindings.
FileSystemServiceBindingLoader takes the root location path and a ParsingStrategy.
The SAP Cloud SDK offers several implementations for the ParsingStrategy as shown in the figure.
EnvironmentVariableServiceBindingLoader
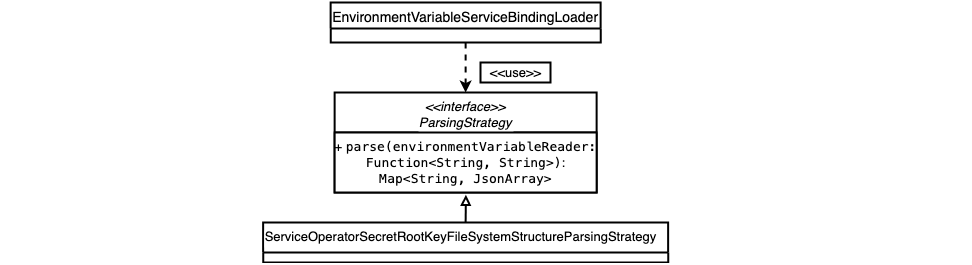
This class is used for transforming environment variables into service bindings based on the provided ParsingStrategy.
It has a Functional Interface (ParsingStrategy), exposing the Map<String, JsonArray> parse(Function<String, String>) method.
EnvironmentVariableServiceBindingLoader.ParsingStrategy represents an algorithm to transform environment variables that can be obtained from the given environment variable reader into service bindings.
EnvironmentVariableServiceBindingLoader takes an environment variable reader and a ParsingStrategy.
The SAP Cloud SDK offers an implementation for the ParsingStrategy as shown in the figure.
ServiceBindingMerger
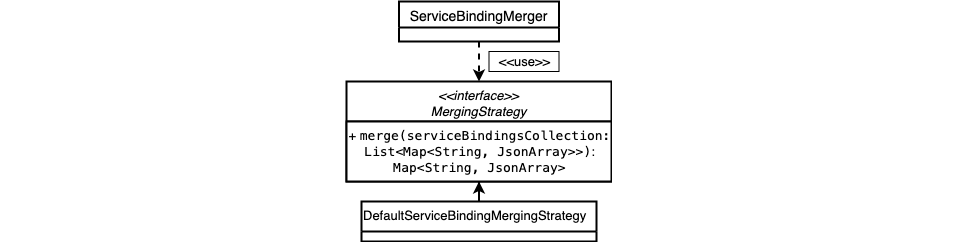
This class is used for merging the result of an arbitrary amount of given instances based on the provided MergingStrategy.
It has a Functional Interface (MergingStrategy), exposing the Map<String, JsonArray> merge(List<Map<String, JsonArray>> serviceBindingsCollection) method.
ServiceBindingMerger.MergingStrategy represents an algorithm to merge multiple service bindings.
ServiceBindingMerger is capable of merging the result of multiple loaders on a binding name (it assumes that each service binding has a property called name) level.
With that, it is able to combine multiple service bindings for the same service from different sources.
SAP Cloud SDK offers an implementation for the MergingStrategy as shown in the figure.
SimpleCachingServiceBindingLoaderWrapper
This class is used for wrapping another instance and caching the result for a certain amount of time.
Once the cache duration has been exceeded, the wrapped ServiceBindingLoader is evaluated again.
The cache can also be reset in a manual fashion.
Usage
The SAP Cloud SDK features can be used in a Kubernetes environment without additional configuration (specifically ScpCfCloudPlatform).
You can load the service binding information by calling the Map<String, JsonArray> getVcapServices() method.
This method enables you to utilize the described architecture without additional configuration.
By default, the service bindings are loaded in the following order:
- Service Operator (Kubernetes) Secret Root Key layout
- Service Operator (Kubernetes) Secret Key layout
- Service Operator (Kubernetes) Data (Default) layout
- VCAP_SERVICES environment variable
This can be customized by providing a ServiceBindingLoader with the method setServiceBindingLoader(ServiceBindingLoader serviceBindingLoader).
Configuration & Customization
The service binding loading has been built with both easy configuration and customization in mind. Therefore, you can tweak the default behavior of the SAP Cloud SDK to fit your needs.
Service Binding Root Location
By default, the DefaultFileSystemStructureParsingStrategy is used under the hood to read and parse file system based service bindings.
It assumes a file system structure like shown below:
/etc/secrets/sapcp/
<service-name#1>/
| <binding-name#1>/
| | - <binding-property#1>
| | - <binding-property#2>
| | - ...
| | - <binding-property#n>
| <binding-name#2>/
| | - ...
... ...
|
<service-name#2>/
|
...
|
<service-name#n>/
There is a root location (/etc/secrets/sapcp by default), which contains an arbitrary amount of sub directories, which each represents a specific service type (e.g. XSUAA or Destination).
Within each of these service specific directories, there are - again - an arbitrary amount of nested folders, each containing one concrete binding for the service type.
While the general directory structure is what we recommend when mounting service bindings to the file system, the root location itself is more like a convention.
Therefore, the SAP Cloud SDK allows for easy configuration:
Path myLocation = Paths.get("my", "custom", "location");
ScpCfCloudPlatform.getInstanceOrThrow().setServiceBindingRootLocation(myLocation);
Overwriting the default root path for service bindings will only take effect when done before accessing any of the service bindings. This is, because the SAP Cloud SDK caches the service bindings indefinitely by default. If you would like to change the service binding root path, we recommend doing it during application startup.