This project is a SwiftUI implementation of the Augmented Reality (AR) patterns in the SAP Fiori for iOS Design Guidelines.
Currently supported:
Requirements
- iOS 15 or higher
- Xcode 14
- Reality Composer 1.1 or higher
- Swift Package Manager
You must configure technical user & password for package resolution!
Dependencies
- SAPCommon for Logging
- SAPFoundation for Network Connectivity and Authentication
- FioriSwiftUI for UI components
Installation
The package is intended for consumption via Swift Package Manager. To add the package to your application target, navigate to File > Add Packages ... >, then add the repository URL.
You can choose one of the following package products to be added to your application/framework target.
| Package Product | When to Use |
|---|---|
| FioriAR | You did not already embed binary frameworks from SAP BTP SDK for iOS |
| FioriAR-requiresToEmbedXCFrameworks | You already embedded SAPCommon and SAPFoundation binary frameworks to your target |
Migration FioriAR 1.0 to FioriAR 2.0
FioriAR 2.0 is NOT fully compatible with the previous version. However, the migration is not difficult. Please follow the migration guide when you prepare to upgrade FioriAR in your project.
AR Annotations
AR Annotations refer to Cards that match with a corresponding Marker located relative to an image or object in the real world. To view annotations in the world view, the user scans the image / object with the AR Scanner.
3D modeling is not required to represent AR annotations as the respective controls (ARScanView, MarkerView and CardView) are implemented with SwiftUI in this package.
An app developer needs to provide a scene of markers relative to an Image or Object anchor. Such scene creation is possible
- within your application by leveraging this package and SAP Mobile Service
- with Apple’s Reality Composer tool
Depending on where and how the scene is stored (.rcproject, .reality, .usdz files or in SAP Mobile Services) the app developer has to specify an appropriate loading strategy to populate the scene and the associated card data.
Cards and Markers support SwiftUI ViewBuilder to allow custom design.
In-App handling relying on SAP Mobile Services
FioriAR provides reusable views and utilities to create/update/delete scenes with AR annotations directly from your app. This is the recommended approach considering how easy it is to create and handle AR annotations.
Scene information will be stored remotely within SAP Mobile Services. As a prerequisite the feature Mobile Augmented Reality needs to be assigned to your application in SAP Mobile Services cockpit.
SAP Mobile Services allows administrators Editing an Augmented Reality Scene which is helpful to maintain AR annotation texts in multiple languages.
Composing the scene
Presenting SceneAuthoringView will provide a user interface in which your users can create AR annotations and specify their positions relatively around an image anchor.
import FioriAR
import SAPFoundation
struct ARCardAuthoringContentView: View {
public var serverUrl: URL
public var sapURLSession: SAPURLSession
public var sceneId: Int? // nil in case of you want to create a new scene
var body: some View {
SceneAuthoringView(title: "Annotations",
serviceURL: serverUrl,
sapURLSession: sapURLSession,
sceneIdentifier: SceneIdentifyingAttribute.id(sceneId))
.onSceneEdit { sceneEdit in
switch sceneEdit {
case .created(card: let card):
print("Card locally created: \(card.title_)")
case .updated(card: let card):
print("Card locally updated: \(card.title_)")
case .deleted(card: let card):
print("Card locally deleted: \(card.title_)")
case .published(sceneID: let sceneID):
print("Scene \(sceneID) created/updated")
}
}
}
}
Viewing the scene
Use ServiceStrategy to fetch scene information from SAP Mobile Services and present its AR annotations in the AR world with ARAnnotationsView.
struct ARCardsServiceView: View {
@StateObject var arModel = ARAnnotationViewModel<CodableCardItem>()
@StateObject var asyncStrategy = ServiceStrategy<CodableCardItem>!
init(serverURL: URL, sapURLSession: SAPURLSession, sceneId: Int) {
_asyncStrategy = ServiceStrategy<CodableCardItem>(
serviceURL: serviceURL,
sapURLSession: sapURLSession,
sceneIdentifier: SceneIdentifyingAttribute.id(sceneId)
)
}
var body: some View {
ARAnnotationsView(arModel: arModel,
cardAction: { id in
print("Action for card \(id) was triggered")
})
.onAppear(perform: loadInitialData)
}
func loadInitialData() {
do {
try self.arModel.loadAsync(loadingStrategy: self.asyncStrategy)
} catch {
print(error)
}
}
}
Reality Composer
FioriAR can handle AR experiences created with Apple’s Reality Composer but the handling of AR annotations is more complex because
- the app developer is responsible on how the app will access files created with Reality Composer
- information shown on AR cards need to be handled outside of Reality Composer
Composing the scene
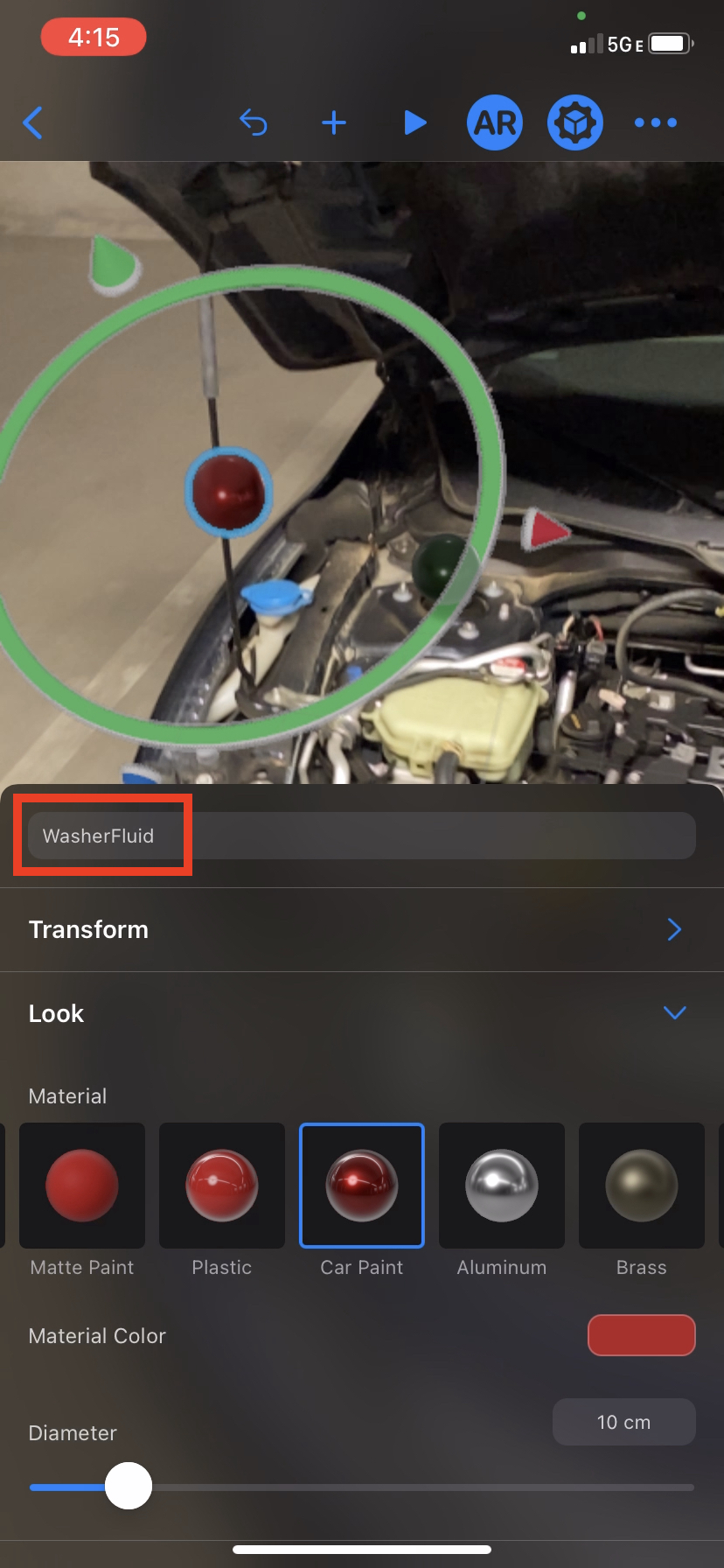
- Open the Reality Composer app and create a scene with an image or object anchor
- Choose an image or scan an object and give the scene a name e.g. ExampleScene
- Place spheres in the desired positions
- Preview in AR to fine tune
- Name the spheres with a type that conforms to LosslessStringConvertable
- The name of the sphere will correspond to the
CardItemModelid - Export the scene either as
.usdzfile (Enable usdz export in preferences or iOS app settings).realityfile or- save the entire project as an
.rcprojectwith a single scene
Notes:
- Reality Composer is required to scan an object when choosing an Object Anchor.
- Scanning an object requires using an iOS device in the Reality Composer app
- The spheres are for scene creation and will be invisible in the ARCards scene

Viewing the scene
This Swift package provides various loading strategies depending on the file format you used to export the scene.
A loading strategy accepts an array of elements, each element conforming to the CardItemModel protocol, to populate card-related data. The id property of the model has to correspond to the name of the Entity (sphere) from Reality Composer.
Each of the loading strategies also has an initializer to accept Data represented by a JSON array.
// JSON key/value:
"id": String,
"title_": String,
"subtitle_": String?,
"detailImage_": Data?, // base64 encoding of Image
"actionText_": String?,
"icon_": String? // systemName of SFSymbol
The supported loading strategies (UsdzFileStrategy, RealityFileStrategy, and RCProjectStrategy) require, in addition to the scene and card-related data, information about the anchor used for detecting a scene. Using an Image anchor requires the app developer to provide anchorImage and its physicalWidth as initializer parameters. For an Object anchor the anchorImage and physicalWidth parameters can be nil.
The scene can be represented in different file types and each strategy requires different data and setup.
- USDZ Strategy: Requires a URL path to the
.usdzfile - Reality Strategy: Requires a URL path to the
.realityfile and the name of the scene - RCProject Strategy: Requires the name of the
.rcprojectfile and the name of the scene
Note:
- The RCProject strategy requires that the
.rcprojectfile is part of the application bundle so that the file is available already during build time. Drag the file into Xcode to do so.
Example Usage: Creating the ContentView and loading the data
import FioriAR
struct FioriARKCardsExample: View {
@StateObject var arModel = ARAnnotationViewModel<CodableCardItem>()
var body: some View {
/**
Initializes an AR Experience with a Scanning View flow with Markers and Cards upon anchor discovery
- Parameters:
- arModel: The View Model which handles the logic for the AR Experience
- guideImage: image to display for anchor detection in the Scanning View, if nil then the image anchor will be used by default
- cardAction: Card Action
*/
ARAnnotationsView(arModel: arModel, guideImage: Image("qrImage"), cardAction: { id in
// action to pass to corresponding card from the CardItemModel id
})
.onAppear(perform: loadInitialData)
}
// Example to use a `UsdzFileStrategy` to populate scene related information (stored in a .usdz file which could have been fetched from a remote server during runtime) as well as card-related information (stored in a .json file which could have been fetched from a remote server as well)
func loadInitialData() {
let usdzFilePath = FileManager.default.getDocumentsDirectory().appendingPathComponent(FileManager.usdzFiles).appendingPathComponent("ExampleRC.usdz")
guard let anchorImage = UIImage(named: "qrImage"),
let jsonUrl = Bundle.main.url(forResource: "Tests", withExtension: "json") else { return }
do {
let jsonData = try Data(contentsOf: jsonUrl)
let strategy = try UsdzFileStrategy(jsonData: jsonData, anchorImage: anchorImage, physicalWidth: 0.1, usdzFilePath: usdzFilePath)
arModel.load(loadingStrategy: strategy)
} catch {
print(error)
}
}
}
How to obtain support
Create a GitHub issue to create bug report, file a feature request or ask a question.
Contributing
If you want to contribute, please check the Contribution Guidelines
Examples
Functionality can be further explored with a demo app which is already part of this package (Apps/Examples/Examples.xcodeproj). See its README for further information.


