Value Help
The administration console of SAP Cloud Identity Services provides a value help feature when an administrator creates restrictions of base policies. For example, using the following base policy:
POLICY ReadProducts {
GRANT read ON products WHERE category IS NOT RESTRICTED;
}An administrator can use the administration console to create an authorization policy that is a restriction of the base policy for a specific category, such as electronics:
POLICY ReadElectronics {
USE ReadProducts RESTRICT category = 'electronics';
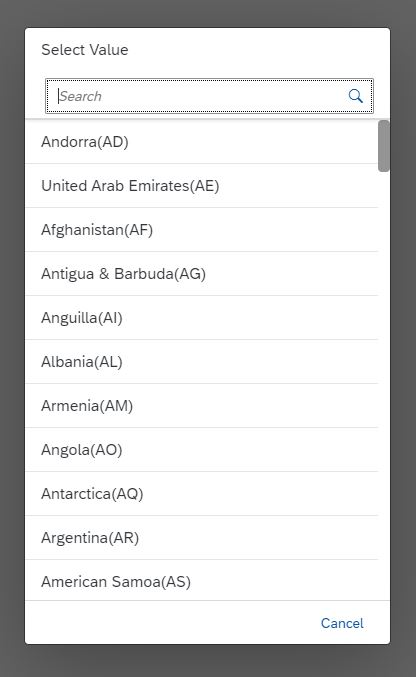
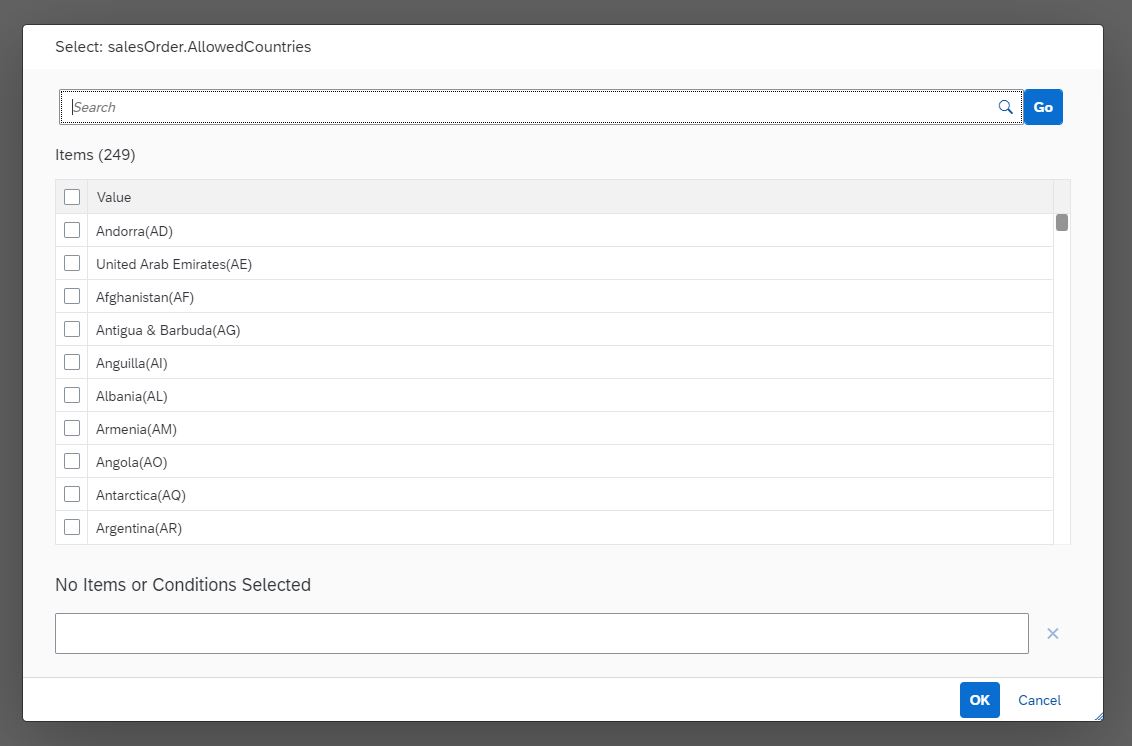
}The value help feature allows the administrator to select the electronics category (or any other category that exists in the application) from a list of available categories. This way, the administrator doesn't have to guess valid values for the category attribute, but can select valid values from a list.
Furthermore, the values can be shown with a human-readable label, such as Electronic Devices instead of showing the raw ID of the values.
Single Select Value Help
Multi Select Value Help
Implementation
To implement the value help feature, the following steps are necessary:
- Implement value help endpoints in the application
- Implement authentication and authorization for the value help endpoints
- Extend the Authorization Management Service (AMS) service instance configuration for value help
- Add value help annotations to attributes in the DCL schema
Sample Implementation
The Node.js CAP Sample contains the required implementations specified below.
Value Help Requests
To retrieve the list of available values for a specific attribute, AMS can be configured to send value help requests to the application. In the response, AMS must receive a list of valid values for the requested attribute from the application and optionally, a human-readable label for each value, which it can then present to the administrator in the administration console.
Request Processing
The AMS service instance is configured with a base URL of the value help service of the application, e.g.
https://your-service.com/odata/v4/value-help.
Then, when AMS requests value help for a specific attribute such as category, by default, it will make a GET request to:
https://your-service.com/odata/v4/value-help/category
TIP
You can customize the path for each attribute using the @valueHelp annotation in the DCL schema, as described in the Annotation Properties section.
Response Format
TIP
CAP services served via the OData protocol implement the requirements below automatically including filtering. You can use projections to define an entity for each attribute inside a dedicated value help service that exposes only the necessary fields (e.g., ID and name) in the response.
The value help endpoints of the application must implement parts of the OData V4 specification to respond with a JSON payload containing the list of available options for the requested attribute.
{
"value": [
{
"ID": "electronics",
"name": "Electronic Devices"
},
{
"ID": "books",
"name": "Books & Media"
}
]
}The response must contain:
value: Array containing the list of available optionsID: The actual value to be used in policies (must fit the DCL attribute data type)name: (optional) human-readable label displayed to administrators (<= 50characters for optimal displayability) instead of the ID
TIP
It is possible to use different property names for the value (ID) and label (name) fields. You can configure these names using the @valueHelp annotation in the DCL schema, as described in the Annotation Properties section.
Request Parameters
Value Help requests contain the following parameters that should be considered when building the response.
Tenant
In multi-tenant applications, if the resulting values depend on the tenant, the application must filter data based on the app_tid claim in the token sent by AMS, as usual.
User Language
If the application supports multiple languages, the Accept-Language header contains the language preferences of the administrator using the administration console. The application can use this information to return localized labels in the response.
Dependent Filters
If the attribute for which value help is requested depends on other attributes, AMS will include the current values of these attributes as OData filter parameters in the request, e.g.
https://your-service.com/odata/v4/value-help/city?$filter=country eq 'DE'
Authorizing Value Help Requests
The value help endpoints in your application MUST be protected because they return business data. To allow the application to authorize value help requests, the AMS server calls the application with an App-To-App principal propagation token based on the administrator who requests value help in the administration console.
API Permission Group
The API permission group consumed by the AMS server can be freely chosen in the service configuration of the AMS instance. It is best practice to setup an internal policy for this API permission group to limit privileges to those that are necessary for the value help endpoints as described in the App-To-App documentation for principal propagation.
Important
Note that such an API policy defines just an upper limit for the privileges that can be used with this token. The administrator using the administration console must additionally have the necessary privileges based on assigned policies to access the value help endpoints in your application.
TIP
Depending on your application, it may not be necessary to create a dedicated new role or action/resource for the value help endpoints. For example, if there is already a policy that grants read access to categories, you can USE this policy in the internal policy for value help.
Certificate Validation
The value help request from the AMS server uses mTLS with a certificate that must be used to validate ownership of the token during authentication.
TIP
The official BTP security libraries for authentication provide the necessary proof-of-ownership validation under the names x5t validation and proof token validation.
Platform-specific certificate handling
As the ingress of the cloud platform terminates TLS, the certificate of the caller needs to be forwarded to your application, by default in the x-forwarded-client-cert header.
If your application is deployed on Cloud Foundry, the .cert domain must be used for the value help callback URL. Cloud Foundry accepts client certificates only on this domain. In this case, it automatically fills the x-forwarded-client-cert header that is used during the validation.
If your application is deployed on Kyma, Istio/Envoy must be configured to forward the client certificate to your application inside the cert= property of the x-forwarded-client-cert header.
AMS Service Configuration
To enable value help functionality, configure your AMS service instance with the value help callback URL and API settings.
Service Instance Configuration
Add the following configuration to your AMS service instance parameters:
authorization:
enabled: true
value-help-url: "https://myapp.cert.cfapps.sap.hana.ondemand.com/odata/v4/value-help/"
value-help-api-name: "AmsValueHelp"
provided-apis:
- name: "AmsValueHelp"
description: "Value Help Callback from AMS"{
"authorization": {
"enabled": true,
"value-help-url": "https://myapp.cert.cfapps.sap.hana.ondemand.com/odata/v4/value-help/",
"value-help-api-name": "AmsValueHelp"
},
"provided-apis": [
{
"name": "AmsValueHelp",
"description": "Value Help Callback from AMS"
}
]
}Configuration Parameters
value-help-url: The base URL of your OData V4 value help service. AMS will append paths of different attributes to this URL when making requests.value-help-api-name: The name of the API that AMS will use for App2App token requests. This must match an entry in theprovided-apissection.provided-apis: Configure a dedicated API for AMS value help.
DCL Annotations
You must enable value help for individual DCL attributes using the @valueHelp annotation in your DCL schema.
Annotation Properties
Configure value help for an attribute as follows:
SCHEMA {
salesOrder: {
@valueHelp: {
path: 'countries',
valueField: 'code',
labelField: 'description'
}
country: String
}
}path: The path appended to the value-help-url when requesting value help for this attributevalueField: Property name in the OData response that contains the valuelabelField: Property name in the OData response that contains the human-readable label
Default Annotation Values
You can omit one or multiple properties of the @valueHelp annotation to use default values. For example:
SCHEMA {
product: {
@valueHelp: {
path: 'categories'
}
category: String
}
}To omit all properties, you can also set @valueHelp to true (or {}):
SCHEMA {
product: {
@valueHelp: true
category: String
}
}In this case, AMS uses these defaults:
- Path: Lowercase version of the attribute name (e.g.,
Category→/category) - Value field:
IDproperty in the response - Label field:
nameproperty in the response
Disabling Value Help
If no @valueHelp annotation is present for an attribute, the value help is disabled for this attribute. For attributes with disabled value help, no button or dialog will be shown in the administration console.
Alternatively, you can set the @valueHelp annotation to false, to explicitly disable the value help for an attribute:
SCHEMA {
product: {
@valueHelp: false
internalId: String
}
}Dependent Attributes
If the valid values for an attribute depend on other attributes, you can configure these dependencies in the @valueHelp annotation using the filters property.
SCHEMA {
salesOrder: {
@valueHelp: {
filters: {
'salesOrder.country': 'country'
}
}
city: String,
country: String
}
}In this example, the valid values for salesOrder.city depend on the value of salesOrder.country. When requesting value help for salesOrder.city, AMS will include the current value of salesOrder.country as a filter parameter with name country in the request if the administrator has already restricted that attribute in the same RESTRICT statement.
For example, given the following state of the RESTRICT statement in the administration console:
POLICY BookGermanTours {
USE BookTours
RESTRICT salesorder.country = 'de', salesorder.city <to be restricted>;
}If the administrator requests value help for salesorder.city, AMS will make the following request to the application:
https://your-service.com/odata/v4/value-help/city?$filter=country eq 'DE'
If an attribute is filtered by more than one other attribute, the filter conditions are combined with and, e.g.
https://your-service.com/odata/v4/value-help/city?$filter=country eq 'DE' and region eq 'BY'
Note
If an attribute defined as filter is not restricted yet, no filter condition will be sent for this attribute.
TIP
The administration console automatically orders the list of attributes in the RESTRICT statement, so that attributes that other attributes depend on are at the top. This works only when there are no circular dependencies between attributes though!
Filter operators
The following list shows how DCL operators are translated into OData filter expressions:
| DCL Operator | OData filter query operator |
|---|---|
| = | eq [value] |
| <> | ne [value] |
| > | gt [value] |
| >= | ge [value] |
| < | lt [value] |
| <= | le [value] |
| BETWEEN | ge [value1] and le [value2] |
| NOT BETWEEN | lt [value1] or gt [value2] |
| IN | in ([values...] ) |
| NOT IN | not(in ([values...])) |
| IS NULL | eq null |
| IS NOT NULL | ne null |
| LIKE | matchesPattern([field], [value]) |
| NOT LIKE | not(matchesPattern([field], [value])) |
| IS RESTRICTED | - (Not relevant for Value Help) |
| IS NOT RESTRICTED | - (Not relevant for Value Help) |