pyrfc¶
The pyrfc package.
PyRFC module functions¶
- pyrfc.get_nwrfclib_version()¶
Get SAP NW RFC Lib version :returns: tuple of major, minor and patch level and OS platform
- pyrfc.set_ini_file_directory(path_name)¶
Sets the directory in which to search for the sapnwrfc.ini file
- Parameters:
path_name (string) – Directory in which to search for the sapnwrfc.ini file.
- Returns:
nothing, raises an error
- pyrfc.reload_ini_file()¶
Reloads the contents of the sapnwrfc.ini file into memory.
Searches the directory given by
RfcSetIniPath()(or the current working directory) for the file sapnwrfc.ini and loads its contents into memory. Reloading the sapnwrfc.ini file is only necessary after the file has been manually edited. If you want to use a sapnwrfc.ini file in a different location, consider usingRfcSetIniPath().Note: If a file with the name
sapnwrfc.inidoes not exist in the given directory, this is not considered an error! Default settings are used in this case.- Returns:
nothing, raises an error
- pyrfc.language_iso_to_sap(lang_iso)¶
Language code conversion of ISO code to SAP code.
- Parameters:
lang_iso (string) – Language ISO code
- Returns:
SAP language code of char 1 type
- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass if ISO to SAP code conversion fails.
- pyrfc.language_sap_to_iso(lang_sap)¶
Language code conversion of SAP code to ISO code.
- Parameters:
lang_sap (string) – Language SAP code
- Returns:
ISO language code
- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass if SAP to ISO code conversion fails.
- pyrfc.set_cryptolib_path(path_name)¶
Sets the absolute path to the sapcrypto library to enable TLS encryption via Websocket Rfc.
The parameter path_name needs also to contain the name of the library. This function has the same effect as the sapnwrfc.ini parameter TLS_SAPCRYPTOLIB. This API cannot reset a new path to the library during runtime. Once set, the path is definitive.
- Parameters:
path_name (string) – Absolute path to crypto library
- Returns:
nothing, raises an error
- pyrfc.set_locale_radix(value=None)¶
Sets the locale radix for decimal conversions.
- Parameters:
value – Locale radix like
.or,- Returns:
New radix set
- pyrfc.cancel_connection(client_connection)¶
Immediately cancels the RFC call which is currently being called over the given RFC connection and closes the connection. Can be used only on an RFC client connection.
RFC call cancellation with timeout can be done automatically, without using this method explicitely. The
timeoutoption can be at connection level, when creating connection instance, or at RFC call level, as RFCConnection.call()option. Either way, the connection will be cancelled if RFC call takes longer thantimeoutseconds.- Parameters:
client_connection (Connection) – RFC client connection instance to be cancelled
- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass thereof if the connection cannot be cancelled cleanly.
Connection¶
- class pyrfc.Connection¶
A connection to an SAP backend system
Instantiating an
pyrfc.Connectionobject will automatically attempt to open a connection the SAP backend.- Parameters:
config (dict or None (default)) –
Configuration of the client connection, valid for all RFC calls of given connection. Allowed keys are:
dtimeABAP DATE and TIME strings are returned as Python datetime date and time objects, instead of ABAP date and time strings (default is False)check_dateCheck the date value before writing to function container (default is True). When deactivated, the validation shall be done by SAP NW RFC SDK and ABAP application.check_timeCheck the time value before writing to function container (default is True). When deactivated, the validation shall be done by SAP NW RFC SDK and ABAP application.rstripright strips strings returned from RFC call (default is True)return_import_paramsimporting parameters are returned by the RFC call (default is False)timeoutCancel connection if ongoing RFC calls takes longer thantimeoutseconds. Timeout can be also set as option for particular RFC call, overriding timeout set at connection level.Examples: https://github.com/SAP/PyRFC/tree/main/examples/timeout
params (Keyword parameters) –
SAP connection parameters. The parameters consist of
client,user,passwd,lang,traceand additionally one ofDirect application server logon:
ashost,sysnr.Logon with load balancing:
mshost,msserv,sysid,group.msservis needed only, if the service of the message server is not defined as sapms<SYSID> in /etc/services.When logging on with SNC,
userandpasswdare to be replaced bysnc_qop,snc_myname,snc_partnername, and optionallysnc_lib. (Ifsnc_libis not specified, the RFC library uses the “global” GSS library defined via environment variable SNC_LIB.)
- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass thereof if the connection attempt fails.
- alive¶
Conection alive property
- Getter:
True when alive
- Type:
boolean
- handle¶
Get client connection handle
- Getter:
Client connection handle
- Type:
uintptr_t
- options¶
Client connection configuration
- Getter:
Client connection options
- Setter:
Set when new connection object created
- Type:
dict
- get_connection_attributes()¶
Get connection details
- Returns:
Mapping of connection information keys:
active_unit: True if there is a filled and submitted unit w/o being confirmed or destroyed.
dest: RFC destination
host: Own host name
partnerHost: Partner host name
sysNumber: R/3 system number
sysId: R/3 system ID
client: Client (“Mandant”)
user: User
language: Language
trace: Trace level (0-3)
isoLanguage: 2-byte ISO-Language
codepage: Own code page
partnerCodepage: Partner code page
rfcRole: C/S: RFC Client / RFC Server
type: 2/3/E/R: R/2,R/3,Ext,Reg.Ext
partnerType: 2/3/E/R: R/2,R/3,Ext,Reg.Ext
rel: My system release
partnerRe: Partner system release
kernelRel: Partner kernel release
cpicConvId: CPI-C Conversation ID
progName: Name calling APAB program (report, module pool)
partnerBytesPerChar: Bytes per char in backend codepage.
partnerSystemCodepage: Partner system code page
reserved: Reserved for later use
Note: all values, except
active_unitare right stripped string values.- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass thereof if the RFC call fails.
- open()¶
Open client the connection
- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass thereof if the connection cannot be opened.
- reopen()¶
Re-open client the connection
- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass thereof if the connection cannot be re-opened.
- call(func_name, options, params)¶
Invokes a remote-enabled function module via RFC.
- Parameters:
func_name (string) – Name of the function module that will be invoked.
options (dictionary) –
Call options for single remote ABAP function call. Allowed keys:
not_requestedAllows to deactivate certain parameters in the function module interface. This is particularly useful for BAPIs which have many large tables, the Python client is not interested in. Deactivate those, to reduce network traffic and memory consumption in your application considerably.This functionality can be used for input and output parameters. If the parameter is an input, no data for that parameter will be sent to the backend. If it’s an output, the backend will be informed not to return data for that parameter.
timeoutCancel RFC connection if ongoing RFC call not completed withintimeoutseconds. Timeout can be also set as client connection configuration option, in which case is valid for all RFC calls.Examples: https://github.com/SAP/PyRFC/tree/main/examples/timeout
params (keyword arguments) – Parameter of the function module. All non optional IMPORT, CHANGING, and TABLE parameters must be provided.
- Returns:
Dictionary with all EXPORT, CHANGING, and TABLE parameters. The IMPORT parameters are also given, if
Connection.config.return_import_paramsis set toTrue.- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass thereof if the RFC call fails.
- close()¶
Close the connection
- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass thereof if the connection cannot be closed cleanly.
- cancel()¶
Cancels the ongoing RFC call using ~pyrfc.cancel_connection() function
- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass thereof if the connection cannot be cancelled cleanly.
- free()¶
Explicitly free connection parameters and close the connection.
Note that this is usually required because the object destruction can be delayed by the garbage collection and problems may occur when too many connections are opened.
- ping()¶
Send a RFC Ping through the current connection
Returns nothing.
- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass thereof if the RFC Ping fails.
- reset_server_context()¶
Resets the SAP server context (“user context / ABAP session context”) associated with the given client connection, but does not close the connection
- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass thereof in case resetting the server context fails. (Better close the connection in that case.).sapnwrf2.CommunicationErrorif no conversion was found for the
- is_valid()¶
Checks an RFC connection. Can be used to check whether a client/server connection has already been closed, or whether the NW RFC library still “considers” the connection to be open.
Note
This does not guarantee that the connection is indeed still alive: A firewall may silently have closed the connection without notifying the endpoints. If you want to find out, whether the connection is still alive, you’ll have to use the more expensive RfcPing().
- Returns:
boolean
- initialize_unit([background=True])¶
Initializes a logical unit of work (LUW), shorthand: unit
Warning
The background protocol (bgRFC) is not working in the current version. Please use only tRFC/qRFC protocols.
- Parameters:
background (boolean) – The bgRFC protocol will be used. If set to False, the t/qRFC protocol will be used. Note that the bgRFC protocol has extended functionality. Default: True
- Returns:
A dictionary describing the unit.
- fill_and_submit_unit(unit, calls[, queue_names=None[, attributes=None]])¶
Fills a unit with one or more RFC and submits it to the backend.
Fills a unit for this connection, prepare the invocation of multiple RFC function modules in it, and submits the unit to the backend.
Afterwards, the unit is still attached to the connection object, until confirm_unit() or destroy_unit() is called. Until one of these methods are called, no other unit could be filled and submitted.
- Parameters:
unit – a unit descriptor as returned by
initialize_unit().calls – a list of call descriptions. Each call description is a tuple that contains the function name as the first element and the function arguments in form of a dictionary as the second element.
queue_names (list of strings or None (default)) –
If the unit uses the background protocol, various queue names can be given (leading to a asynchronous unit, type ‘Q’). If parameter is an empty list or None, a synchronous unit (type ‘T’) is created.
If the unit does not use the background protocol, the queue name may be a list with exactly one element, leading to a qRFC, or an empty list or None, leading to a tRFC.
attributes (dict or None (default)) –
optional argument for attributes of the unit – only valid if the background protocol is used. The attributes dict may contain the following keywords:
keyword
default
type
description
kernel_trace
0
int
If != 0, the backend will write kernel traces, while executing this unit.
sat_trace
0
int
If != 0, the backend will write statistic records, while executing this unit.
unit_history
0
int
If != 0, the backend will keep a “history” for this unit.
lock
0
int
Used only for type Q: If != 0, the unit will be written to the queue, but not processed. The unit can then be started manually in the ABAP debugger.
no_commit_check
0
int
Per default the backend will check during execution of a unit, whether one of the unit’s function modules triggers an explicit or implicit COMMITWORK. In this case the unit is aborted with an error, because the transactional integrity of this unit cannot be guaranteed. By setting “no_commit_check” to true (!=0), this behavior can be suppressed, meaning the unit will be executed anyway, even if one of it’s function modules “misbehaves” and triggers a COMMIT WORK.
user
current operating system user
String, len 12
Sender User (optional).
client
”000”
String, len 3
Sender Client (“Mandant”) (optional).
t_code
””
String, len 20
Sender Transaction Code (optional).
program
current executable name
String, len 40
Sender Program (optional).
- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass thereof if an error occurred. In this case, the unit is destroyed.
- confirm_unit(unit)¶
Confirm the current unit in the backend.
This also destroys the unit.
- Parameters:
unit – a unit descriptor as returned by
initialize_unit().- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass thereof if the connection attempt fails.
- destroy_unit(unit)¶
Destroy the current unit.
E.g. if the completed unit could not be recorded in the frontend.
- Parameters:
unit – a unit descriptor as returned by
initialize_unit().- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass thereof if the connection attempt fails.
- get_unit_state(unit)¶
Retrieves the processing status of the given background unit.
Note
Only available for background units.
- Parameters:
unit – a unit descriptor as returned by
initialize_unit().- Returns:
The state of the current bgRFC unit. Possible values are: RFC_UNIT_NOT_FOUND RFC_UNIT_IN_PROCESS RFC_UNIT_COMMITTED RFC_UNIT_ROLLED_BACK RFC_UNIT_CONFIRMED
- get_function_description(func_name)¶
Returns a function description of a function module.
- Parameters:
func_name (string) – Name of the function module whose description will be returned.
- Returns:
A
FunctionDescriptionobject.
- type_desc_get(type_name)¶
Removes the Type Description from SAP NW RFC Lib cache
- Parameters:
type_name (string) – system id (connection parameters sysid)
- Returns:
error code
- type_desc_remove(type_name)¶
Removes the Type Description from SAP NW RFC Lib cache
- Parameters:
sysid (string) – system id (connection parameters sysid)
type_name – Name of the type to be removed
- Returns:
error code
- func_desc_remove(func_name)¶
Removes the Function Description from SAP NW RFC Lib cache
- Parameters:
sysid (string) – system id (connection parameters sysid)
func_name (string) – Name of the function module to be removed
- Returns:
error code
Server¶
- class pyrfc.Server¶
An ABAP server
An instance of
Serverallows for installing Python callback functions and serve requests from SAP systems.- Parameters:
server_params (dict) – Parameters for registering Python server. The parameters may contain the following keywords:
GWHOST`, ``GWSERV,PROGRAM_ID,TRACE, andSAPROUTER.client_params – Parameters for Python client connection. The parameters may contain the following keywords:
GWHOST`, ``GWSERV,PROGRAM_ID,TRACE, andSAPROUTER.config (dict or None (default)) –
Configuration of server instance. Allowed keys are:
dtimeABAP DATE and TIME strings are returned as Python datetime date and time objects, instead of ABAP date and time strings (default is False)check_dateCheck the date value before writing to function container (default is True). When deactivated, the validation shall be done by SAP NW RFC SDK and Python application.check_timeCheck the time value before writing to function container (default is True). When deactivated, the validation shall be done by SAP NW RFC SDK and Python application.rstripright strips strings returned from RFC call (default is True)debugFor testing/debugging operations. If True, the server behaves more permissive, e.g. allows incoming calls without a valid connection handle. (default is False)
- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass thereof if the connection attempt fails.
- bgrfc_init(sysId, bgRfcFunction)¶
Installs the necessary callback functions for processing incoming bgRFC calls.
These functions need to be implemented by Python application and will be used by the RFC runtime. When no callback function is provided, the default one is used, not necessarily matching your application requirements.
For more info search for the
RfcInstallBgRfcHandlersmethod in SAP NetWeaver RFC SDK Doxygen Documentation- Parameters:
sysId (string or None) – System ID of the SAP system for which to use this set of transaction handlers, or None When None value provided, the transaction handlers will be used for bgRFC calls from any backend system, for which no explicit handlers have been installed.
bgRfcFunction – Function callbacks
- Returns:
error code, zero when no error
- add_function(func_name, callback)¶
Installs a function in the server.
- Parameters:
func_name (string) – ABAP remote function module name
callback – A callback function that implements the logic. The function must accept a
request_contextparameter and all IMPORT, CHANGING, and TABLE parameters of the givenfunc_desc.
- Raises:
RFCErrorif a function with the name given is already installed.
- serve()¶
Starts the RFC server, waiting for incoming requests and processes them.
- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass thereof if the server processing fails.
- start()¶
Start the RFC server in new thread, waiting for incoming requests and processes them.
- stop()¶
Stop the RFC server thread.
- close()¶
Explicitly close the registration. Note that this is usually not necessary as the registration will be closed automatically upon object destruction. However, if the the object destruction is delayed by the garbage collection, problems may occur when too many servers are registered.
- get_server_attributes()¶
Retrieves detailed information about a multi-count Registered Server or a TCP Socket Server.
- Returns:
Dictionary with server state and attributes
- Return type:
dict(str, str or int)
serverName: This server’s name as given when creating the server.
protocolType: This RFC server’s type: RFC_MULTI_COUNT_REGISTERED_SERVER or RFC_TCP_SOCKET_SERVER
registrationCount: The current number of active registrations (in case of a Registered Server) or the maximum number of parallel connections the server will accept (in case of a TCP Socket Server)
state: Used in state information in order to indicate the current state of an RFC Server.
currentBusyCount: The number of requests currently being processed.
peakBusyCount: The maximum number of requests the server has been processing in parallel since it has been created
Connection Parameters¶
- class pyrfc.ConnectionParameters¶
Connection parameters instance in SAP unicode format
- Parameters:
args (positional) – Connection parameters like ASHOST=”ABC” etc
- Returns:
Nothing
Function Description¶
Note
Actually, the FunctionDescription class does not support exceptions.
- class pyrfc.FunctionDescription(name)¶
A function description
This class wraps the RFC_FUNCTION_DESC_HANDLE as e.g. returned by RfcGetFunctionDesc() and used for server functionality.
Warning
Actually, the function description does not support exceptions (cf. RfcAddException() etc.)
- Parameters:
name – Name of the function.
Attributes and methods
- name
The name of the function.
- parameters
The parameters as a list of dicts.
- add_parameter(name, parameter_type, direction, nuc_length, uc_length[, decimals=0[, default_value=""[, parameter_text=""[, optional=False[, type_description=None]]]]])¶
Adds a parameter to the function description.
- Parameters:
name (string (30)) – Parameter name
parameter_type (string) – RfcFieldType enum name
direction (string) – RfcParameterDirection enum name
nuc_length (int) – NUC length
uc_length (int) – UC length
decimals (int) – Decimals (default=0)
default_value (string (30)) – Default value (default=””)
parameter_text (string (79)) – Parameter text (default=””)
optional (bool) – Is the parameter optional (default=False)
type_description (object of class TypeDescription) – An object of class TypeDescription or None (default=None)
Type Description¶
- class pyrfc.TypeDescription(name, nuc_length, uc_length)¶
A type description
This class wraps the RFC_TYPE_DESC_HANDLE as e.g. contained in a parameter description of a function description.
- Parameters:
name – Name of the type.
nuc_length – Length of the type in non unicode systems.
uc_length – Length of the type in unicode systems.
Attributes and methods
- name
The name of the function.
- nuc_length
The length in bytes if chars are non unicode.
- uc_length
The length in bytes if chars are unicode.
- fields
The fields as a list of dicts.
- add_field(name, field_type, nuc_length, uc_length, nuc_offset, uc_offset[, decimals=0[, type_description=None]])¶
Adds a field to the type description.
- Parameters:
name (string (30)) – Field name
field_type (string) – RfcFieldType enum name
nuc_length (int) – NUC length
uc_length (int) – UC length
nuc_offset (int) – NUC offset.
uc_offset (int) – UC offset.
decimals (int) – Decimals (default=0)
type_description (object of class TypeDescription) – An object of class TypeDescription or None (default=None)
Throughput¶
- class pyrfc.Throughput¶
- _handle¶
Get throughput object handle
- Getter:
Throughput object handle
- Type:
uintptr_t
- connections¶
Get connections attached to throughput monitoring
- Getter:
Connections’ instances
- Type:
set of Connection
- stats¶
Get throughput monitor statistics
- Getter:
Throughput monitor counters
- Type:
dict(str,int)
numberOfCalls
sentBytes
receivedBytes
applicationTime
totalTime
serializationTime
deserializationTime
- setOnConnection()¶
Attaches a throughput object to a connection to be monitored by the throughput object. Once attached to a connection, the throughput object collects the data statistics of function calls invoked via this connection.
For more info search for the
RfcSetThroughputOnConnectionmethod in SAP NetWeaver RFC SDK Doxygen Documentation- Parameters:
connection (Connection) – Connection instance to be attached to throughput monitoring
- Returns:
nothing, raises an error
- static getFromConnection()¶
Returns the currently attached throughput object from a connection, if any.
For more info search for the
RfcGetThroughputFromConnectionmethod in SAP NetWeaver RFC SDK Doxygen Documentation- Parameters:
connection (Connection) – Connection instance
- Returns:
Throughput object the connection is attached to, if any
- Return type:
- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass in case of error
- removeFromConnection()¶
Removes the throughput object from a connection. The connection will no longer be monitored.
- Parameters:
connection (Connection) – Connection instance
- Returns:
Nothing
- Raises:
RFCErroror a subclass in case of error
Errors¶
If a problem occurs in the Python connector or in an underlying component (e.g. C connector, SAP system, ABAP code, …), an exception is raised. The class of the exception indicates where the problem occurred.
RFCError: This error is raised, if a problem occurred in the Python connector.RFCLibError: This error is raised, if a problem occurred in the C connector.All other errors represent errors with the RFC call to the SAP backend system. For these errors, the errorInfo struct of the C connector is wrapped, e.g. for a given exception
e, the error code is available ine.code. The class of the error depends on the group of the error.
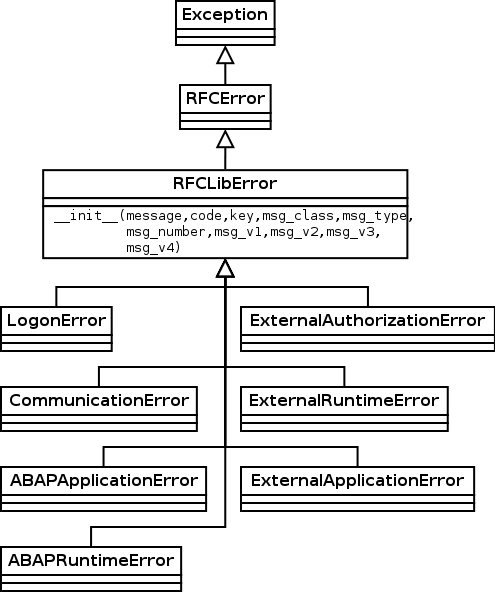
- exception pyrfc.RFCError¶
Exception base class.
Indicates that there was an error in the Python connector.
- exception pyrfc.RFCLibError(message=None, code=None, key=None, msg_class=None, msg_type=None, msg_number=None, msg_v1=None, msg_v2=None, msg_v3=None, msg_v4=None)¶
RFC library error.
Base class for exceptions raised by the local underlying C connector (sapnwrfc.c).
- exception pyrfc.LogonError(message=None, code=2, key='RFC_LOGON_FAILURE', msg_class=None, msg_type=None, msg_number=None, msg_v1=None, msg_v2=None, msg_v3=None, msg_v4=None)¶
Logon error.
This exception is raised if a RFC call returns an RC code greater than 0 and the error object has an RFC_ERROR_GROUP value of LOGON_FAILURE.
- exception pyrfc.CommunicationError(message=None, code=None, key=None, msg_class=None, msg_type=None, msg_number=None, msg_v1=None, msg_v2=None, msg_v3=None, msg_v4=None)¶
Communication error.
This exception is raised if a RFC call returns an RC code greater than 0 and the error object has an RFC_ERROR_GROUP value of COMMUNICATION_FAILURE.
- exception pyrfc.ABAPApplicationError(message=None, code=None, key=None, msg_class=None, msg_type=None, msg_number=None, msg_v1=None, msg_v2=None, msg_v3=None, msg_v4=None)¶
ABAP application error.
This exception is raised if a RFC call returns an RC code greater than 0 and the error object has an RFC_ERROR_GROUP value of ABAP_APPLICATION_FAILURE.
- exception pyrfc.ABAPRuntimeError(message=None, code=None, key=None, msg_class=None, msg_type=None, msg_number=None, msg_v1=None, msg_v2=None, msg_v3=None, msg_v4=None)¶
ABAP runtime error.
This exception is raised if a RFC call returns an RC code greater than 0 and the error object has an RFC_ERROR_GROUP value of ABAP_RUNTIME_FAILURE.
- exception pyrfc.ExternalAuthorizationError(message=None, code=None, key=None, msg_class=None, msg_type=None, msg_number=None, msg_v1=None, msg_v2=None, msg_v3=None, msg_v4=None)¶
External authorization error.
This exception is raised if a RFC call returns an RC code greater than 0 and the error object has an RFC_ERROR_GROUP value of EXTERNAL_AUTHORIZATION_FAILURE.
- exception pyrfc.ExternalRuntimeError(message=None, code=None, key=None, msg_class=None, msg_type=None, msg_number=None, msg_v1=None, msg_v2=None, msg_v3=None, msg_v4=None)¶
External runtime error.
This exception is raised if a RFC call returns an RC code greater than 0 and the error object has an RFC_ERROR_GROUP value of EXTERNAL_RUNTIME_FAILURE.
- exception pyrfc.ExternalApplicationError(message=None, code=None, key=None, msg_class=None, msg_type=None, msg_number=None, msg_v1=None, msg_v2=None, msg_v3=None, msg_v4=None)¶
External application error.
This exception is raised if a RFC call returns an RC code greater than 0 and the error object has an RFC_ERROR_GROUP value of EXTERNAL_APPLICATION_FAILURE.
Error types, codes, groups, and classes¶
Schmidt and Li (2009a) describe four possible error types on the basis of the return code (i.e. error code) of a RFM invocation:
ABAP exception,
system failure,
ABAP messages, and
communication failure.
However, there are in total roughly 30 possible return codes that indicate some kind of error. As each error information struct provides an error group information with seven possible groups, which was taken as the basis for the exception classes.
The following table should facilitate the matching between the different error representations.
type (SPJ) |
code [numeric] (C) |
group (C) |
class (Python) |
|---|---|---|---|
ABAP exception |
RFC_ABAP_EXCEPTION [5] |
ABAP_APPLICATION_FAILURE |
ABAPApplicationError |
system failure |
RFC_ABAP_RUNTIME_FAILURE [3] |
ABAP_RUNTIME_FAILURE |
ABAPRuntimeError |
ABAP message |
RFC_ABAP_MESSAGE [4] |
ABAP_RUNTIME_FAILURE |
ABAPRuntimeError |
communication failure |
RFC_COMMUNICATION_FAILURE [1] |
COMMUNICATION_FAILURE |
CommunicationError |
RFC_LOGON_FAILURE [2] |
LOGON_FAILURE |
LogonError |